Form groups to include students who had investigated Reaction A and Reaction B in the BCE.
1. Compare the chemical equations that describe the overall reaction that occurred in Reaction A and Reaction B.
2. Compare the mechanisms that describe the overall reaction that occurred in Reaction A and Reaction B.
3. Using the data from Question 4 in the BCE compare the rates of Reaction A and Reaction B.
4. In Reaction B
a) does R fulfil the characteristics of a reactant in the overall reaction? Explain.
b) does R fulfil the characteristics of a product in the overall reaction? Explain.
c) does R fulfil the characteristics of an intermediate in the overall reaction? Explain.
d) What are the characteristics of R in the overall reaction? In the mechanism of the reaction? Explain.
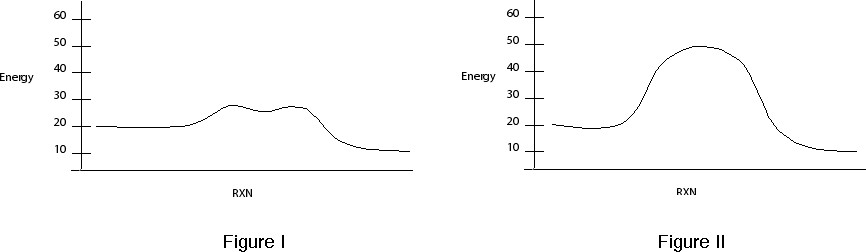
Figures I and II depict Reaction Coordinate diagrams. Which Reaction Coordinate diagram best describes Reactions A? Reaction B?
Label the reactants and products in both diagrams. Estimate the activation energies for Reaction A and B.
Based on the activation energies for the two reactions how do explain the difference rates. How do the differences in the mechanisms for Reaction A and B
Construct an explanation that you could use to explain to another group the chemical characteristic of R and how R effects the rate of a chemical reaction. Use some or all of the following terms in your explanation: reactants, products, intermediate, catalyst, activation energy, reaction mechanism, alternative reaction pathway, increasing rate, decreasing rate, activated complex, exothermic, endothermic, enthalpy change, early step of a mechanism and a subsequent step in the mechanism, connections between the the overall reaction, the mechanism of a reaction and the reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction.
Clicker Questions: Show a mechanism and ask students to identify reactants, prducts, intermediates, catalysts, etc.
