, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,
CHEM 1314 Spring 2009 ACA2 Response Page
This is ACA # 2, our first ACA of the Fall semester. It is OK
to use your textbook, but if you can answers the questions without it that is
OK too.
I recommend you print out this page and bring it to class. Click
here to show a set of five ACA2 student responses, randomly selected from
all of the student responses thus far, in a new window.
, here are your responses
to the ACA and the Expert's response.
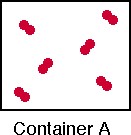
1. Consider the contents of Container A and complete parts a - d below.
 |
You have characterized the contents of the container as;
a)
b)
c)
d)
This container shows an element
(a pure substance) as a diatomic molecule in the gas phase. |
| |
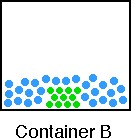
2. Consider the contents of Container B and complete parts a - c below.
 |
a) Indicate the type of mixture in the container;
b) For the blue component;
i)
ii)
iii)
c) For the green component;
i)
ii)
iii)
The container shows an atomic element in the solid phase
(green color) in a liquid phase of another atomic element (blue). The solid (green) is undissolved in the liquid (blue),
so this is a heterogeneous mixture. (NOTE: If the solid dissolved the mixture
would be homogeneous.) |
|
3. Consider the contents of Container C and Container D and complete parts a - b below.
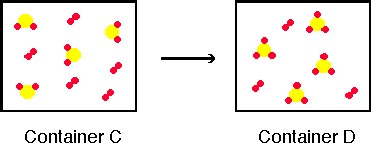 |
a) Consider the change that occurs from Container C to Container D;
Container C on the left (reactants) shows a compound
(yellow atom with two red atoms covalently bonded to it) and an element (the
diatomic red molecule). Both substances are gases so the mixture is homogeneous.
Container D on the right has a new compound (yellow atom with three red
atoms covalently bonded to it) and an element (the same diatomic molecule
found in the container on the left). These two containers taken together represent
a chemical reaction. Notice two of the R2 molecules in Container C have reacted, leaving three unreacted R2 molecules.
b) Which of the following best describes the change that occurs;
In Container C the reactants are YR2 and R2. In Container D the product of the reaction is YR3. Container D also contains R2 but it has already been labeled as a reactant. So the equation we could write to describe the reaction is;
YR2 + R2 ---> YR3
but this equation is not balanced, balancing the equation we would get;
2YR2 + R2 ---> 2YR3
That particular form of the equation is not a choice from the list, but 2SO2 + O2 ---> 2SO3 is a choice, so assuming atom Y is sulfur and atom R is oxygen the best chemical equation to write to represent the reaction, is;
2SO 2 + O2 ---> 2SO3
|
|
4. Without looking at your textbook complete the following table about elements;
Symbol |
Name |
Formula |
Phase (at 25 °C) |
Al
|
aluminum
|
Al
|
solid
|
N
|
nitrogen
|
N2
|
gas
|
Br
|
bromine
|
Br2
|
liquid
|
5a. Describe what happened when the piece of sodium
metal is added to the chlorine gas? (Note: Here is another movie of the reaction.) (Here is the link to the page in your VitaSource ebook.) Either movie will be opened in a new window. After watching
the movie close the window to get back to the ACA. (If the movie does not work see page 42 in your textbook.)
(NOTE: The video is in QuickTime format so you must have that player. I recommend getting iTunes as it also has the QuickTime Player. Also with iTunes you will be able to subscribe to the CHEM 1314 video podcasts that contain lectures, problem solving videos and other cool features. See the Announcements Page for more info on podcasts.)
When the solid, silvery sodium metal was added to
greenish-yellow an immediate reaction occurred as evidenced by the bright
yellow flame that appeared in the container. As the yellow flame diminished
a white cloud of sodium chloride was observed.
b) Write a chemical equation to describe the reaction in Q5a. (NOTE: Your chemical
equation should use formulas for the reactants and for the product, and each substance's phase
should be identified as (g)as, (l)iquid, (s)olid or (aq)ueous.)
When writing chemical equations, we must always use the formulas for each reactant and product. The correct formula for the element sodium is Na, and for the element chlorine, Cl2. The phases are aso useful to include. The correct formula for the product is a little more complicated and will be a topic of further discussion in class. In this case sodium is a metal (likes to lose electrons) in Group I and chlorine is a nonmetal (likes to gain electrons) in Group VII. As we will learn shortly Group I metals like to lose one electron and Group VII nonmetals like to gain one electron, so the correct formula of the product (with balanced charges) is NaCl.
So the complete equation would be: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) ----> 2NaCl(s)
6. Is there anything about the questions that you feel you do not understand?
List your concerns/questions.
7. If there is one question you would like to have answered in lecture,
what would that question be?



