Learning Objectives |
BCE |
DCI |
ACA |
Link |
Download |
Type |
LO 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4 , 8.5 |
|
|
|
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/BCE38.php
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/ACA44.php |
|
QuickTime |
LO 8.11 |
|
|
|
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/BCE39.php
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/ACA45.php |
|
|
LO 8.12, 8.13, 8.14, 8.15, 8.16 |
|
|
|
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/BCE40.php
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/ACA46.php
|
|
mp4 movie |
LO 8.12, 8.13, 8.14, 8.15, 8.16 |
|
|
|
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/BCE41.php
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/ACA47.php |
|
|
LO 8.6, 8.7 |
|
|
|
http://genchem1.chem.okstate.edu/BDA/BCE42.php
h |
|
Solution Process in terms of 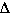 G° = G° = 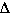 H° - T H° - T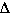 S° S° |