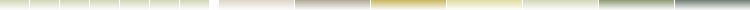Welcome to The Acid/Base chemistryweb-site
The third Scientist is Gilbert Newton Lewis,1923 ,and his theory about acid/base. lewis theory deals with the way in which a substance Accepts or Donates a pair of electrons in an acid-base type of reaction.
Lewis Acid is an electron pair acceptor.Lewis Base is an electron pair donor.
In The Reaction Below Between H+ and Ammonia.
Ammonia, NH3 will act as a Lewis Base (electron pair donor) when reacts with a metal cation or (electron deficient atom) like (H+) which will act as Lewis Acid (electron pair acceptor)to form a complex ion NH4+ .
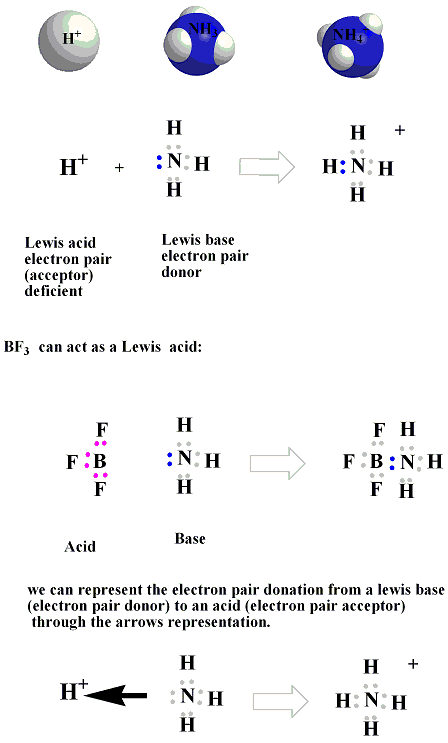
In The Reaction below between BF3 and NH3, BF3 acts as Lewis Acid with an incomplete octet of electrons, so it has a vacant orbital in its valence shell in which it will accept the lone pair of electrons from NH3Lewis Base.

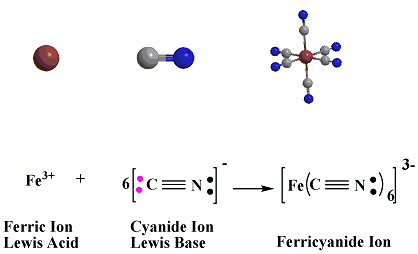
In the reaction below between Ferric Ion Lewis Acid or (electron pair acceptor), as it has a vacant orbitals that can accept the electron pairs donated by the cyanide ions Lewis Base.
Species acting as Lewis acids (e.g. Cu2+ , Zn2+) need not be Bronsted acids(proton donors). in that sense the lewis model broadens the concept of an acid.
Species that act as Lewis bases or (electron pair donor) (e.g. H2O , NH3 , OH- ) are also Bronsted-Lowry Bases or (Proton Acceptor) as it must have unshared pair of electrons for binding the proton.
The Advantage of The Lewis Theory
using Lewis Theory can explain A wide Variety of Reactions, including the reactions in which there is no Proton transfer.
Acid-Base Topics
- Acid-Base Topics
- Tutorials
- Experiments
- Questions
- Home
Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Experiments
- Litmus paper experiment
this experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of Litmus paper, it also shows the difference between Bronsted-lowry acid and base. - Indicator experiment
This experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of a n Acid-Base indicator.
- Acid-Base pH meter titration Experiment
Wide selection of Brother Ink Cartridges - Acid-Base Titration experiment
Web Hosting for 10 Websites