Welcome to The Acid/Base chemistryweb-site
In this website we will discuss the chemistry of acids and bases. Acids and bases can be considered as the most important chemicals in our lives, so we will take a closer look at acids and bases and their general characteristics. We will start with the general characteristics of acids.
General Characteristics of Acids.
General Characteristics of Bases
Postulated Theories for Acid-Base Definition
There are three different definitions that are used to describe
acids and
bases. These definitions based on Arrhenius
theory, Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base
theory, and
Lewis Theory.
The classification of substances as either acids or bases began when
the
Swedish chemist, Svante Arrhenius ,in 1884,
proposed the first scientific
definition of acids and bases.
Arrhenius defined an acid as any substance that
contains hydrogen and when
dissolved in an aqueous solution produces
hydrogen ions (protons, H+)
and anions.
Note: H+(aq.) ion is a proton with no surrounding valence electrons.
in water, clusters of hydrated H+ ions exist in the form
of hydronium
ion (H3O+).
Models Of Arrhenius Acids
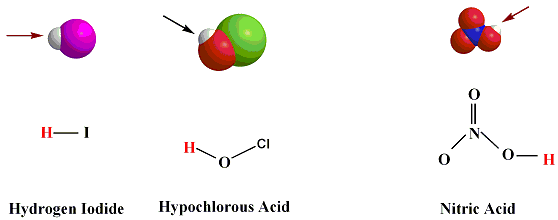
In writing the acid formula, we need to write
the formula of the H
atom first before the anion formula. The arrows
in the Figure above
point towards the hydogen atom in Arrhenius acids.
Examples of acids. HF, HI, HCl, H3O+, H3PO4,
HNO3, are all acids. NO3-,
PO43-
are not acids.
HI (aq)  H+(aq) + I- (aq)
H+(aq) + I- (aq)
We have to be careful, just because a compound contains hydrogen
or
a hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom, does not mean the compound
will
behave as an acid. For example:
Types of hydrogen Atoms:
Arrhenius definition of a base (metal hydroxide)
M(OH)n: Is a substance that contains
a metal and hydroxide
group (OH-) and produces hydroxide ions (OH-)
in the
aqueous solution. Arrhenius base increases the OH-
concentration in water.
Arrhenius base can be represented by the formula
M(OH)n . where M stands
for a metal atom, and (OH-)
is the hydroxide ions.
NaOH  Na+ + OH-
Na+ + OH-
Acid-Base reactions involve proton transfers.
Acid And Base Topics
- Acid-Base identification Activity
- Acid-Base Identification activity
- Acid And Base Topics
- Acid/ Base characteristics/ Arrhenius theory.
- Acid/Base Arrhenius theory limitations.
- Bronsted-Lowry A/B theoryI.
- Bronsted-Lowry A/B theoryII.
- Lewis Acid/Base theory
- Acid And Base Topics
- Acid-Base strength I.
- Acid-Base strength II.
- A/B Arrhenius Theory Question
- Acid/Base question.1.
- Quiz
- Acid-Base Quiz
Pre-Classroom Activity and Experiments
- Litmus paper experiment
this experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of Litmus paper, it also shows the difference between Bronsted-lowry acid and base. - Indicator experiment
This experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of a n Acid-Base indicator.
- Acid-Base pH meter titration Experiment
this experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of Litmus paper, it also shows the difference between Bronsted-lowry acid and base. - Acid-Base Titration experiment
This experiment explores the effect of different chemicals on the color change of a n Acid-Base indicator.